General information
- Stamp Duty Relief for Employment Contracts
- Employment contracts signed before 1 January 2025 are exempt from stamp duty.
- The relief does not explicitly extend to other agreements like service or intragroup service agreements; businesses should carefully review these in light of increased IRBM scrutiny.
- For employment contracts signed during 2025, businesses have until 31 December 2025 to comply with stamping requirements.
- Companies should assess associated employment documents (e.g., increment letters) for stamp duty obligations under the Stamp Act 1949.
- Self-Assessment for Stamp Duty takes effect from 1 January 2026, so a broad compliance review is recommended beyond just employment contracts.
- Restriction on Consolidated e-Invoices
- Consolidated e-Invoices (which require less buyer data) are banned for transactions over RM10,000 starting 1 January 2026.
- Until 31 December 2025, consolidated e-Invoices remain permitted for transactions above RM10,000, except where transaction-specific e-Invoices are mandatory (e.g., motor vehicle sales, flight tickets, private charters, construction, and related materials).
- e-Invoicing Deferral and Exemptions
- The revenue threshold for exemption from e-Invoicing increases from RM150,000 to RM500,000, applicable to both incorporated and unincorporated businesses.
- If a payee is an individual not conducting business, payers must issue a Self-Billed e-Invoice (SBeI), regardless of income level.
- The e-Invoicing timeline for businesses with annual revenue ≤ RM5 million is delayed by six months.
- Updated e-Invoicing Timeline
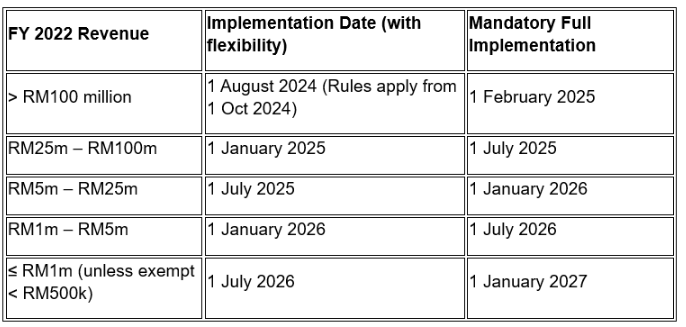
Notes:
- During the initial 6-month phase, consolidated e-Invoices are broadly permitted but non-compliance still triggers penalties.
- The RM500,000 exemption threshold is assessed annually. If crossed, e-Invoicing applies from Year 3.
- Group companies may be excluded from exemption.
- New businesses post-2022 follow a default start date of 1 July 2026, subject to exemptions.
Analysis:
- These updates signal IRBM’s stricter oversight on both stamp duty and digital tax reporting.
- Employers and businesses must conduct comprehensive reviews, especially regarding contracts, group structures, and transaction values.
- The phased e-Invoicing rollout provides flexibility, but businesses should not delay preparations given penalties still apply during transition periods.
- Particular attention is required for fragmented payments, individual recipients, and ensuring proper issuance of SBeI where needed.
Other news from Other countries
Chile Reminder: Deadline Approaching for Document Printing Issues: March 1, 2026
 Other countries
Author: Ema Stamenković
Other countries
Author: Ema Stamenković
The deadline to print required documents is March 1st, 2026. Resolution No. 12 mandates companies to provide printed electronic invoices and receipts, effective May 1st, 2025, alongside digital transmission options. The deadline for anyone who is unable to print the required documents due to a lack of equipment or an unconfigured system is March 1st, 2026. The resolution No.12 that was published o... Read more



China Implements New VAT Law Regulations
 Other countries
Author: Ljubica Blagojević
Other countries
Author: Ljubica Blagojević
China’s VAT implementation regulations, effective 1 January 2026, replace the provisional VAT rules and introduce tighter VAT scope and input VAT credit rules, including annual reconciliation for long-term assets over RMB 5 million (approx. €605,404). While VAT rates remain unchanged, compliance complexity increases, and businesses should reassess VAT positions and controls ahead of implementation... Read more



Colombia Approves Temporary 2026 Tax Hikes on Alcohol, Tobacco, and Imports
 Other countries
Author: Ema Stamenković
Other countries
Author: Ema Stamenković
The Colombian Government issued Decree 1474 due to an Economic Emergency, introducing temporary tax measures for 2026 to address a fiscal gap. VAT and excise tax increases apply to liquor, cigarettes, and certain vehicles. Equity tax threshold lowered and progressive rates increased. A special 1% tax on hydrocarbons/coal is extended, and a 19% normalization tax on undeclared assets initiates. Pena... Read more



UAE VAT Rates Overview
 Other countries
Author: Ema Stamenković
Other countries
Author: Ema Stamenković
UAE VAT is crucial for businesses, with a standard rate of 5% on most goods/services. Zero-rated supplies allow input VAT recovery, while exempt supplies incur hidden costs. Compliance and documentation are essential for strategic business insights. Value-Added Tax (VAT) is essential for businesses in the UAE. Understanding rates and compliance impacts your bottom line. Standard Rate: 5% Applies... Read more



Saudi Arabia Extends Tax Penalty Waiver to June 2026
 Other countries
Author: Ema Stamenković
Other countries
Author: Ema Stamenković
On 1 January 2025, Saudi Arabia extended ZATCA’s initiative to cancel penalties for taxpayers until June 2026. Eligible taxpayers must submit returns and pay dues, excluding evasion penalties and those already paid. On 1 January 2025, Saudi Arabia’s Minister of Finance approved a six-month extension of ZATCA’s Initiative to Cancel Fines and Exempt Taxpayers from Financial Penalties. Th... Read more



New Zealand E-Invoicing Overview
 Other countries
Author: Ema Stamenković
Other countries
Author: Ema Stamenković
New Zealand is rolling out e-invoicing in phases, emphasizing government procurement and using the Peppol framework. While adoption is voluntary for businesses, large suppliers will be mandated to send e-invoices by January 1, 2027. E-invoices must follow the Peppol BIS Billing 3.0 specification and include essential GST-related information. The focus is solely on domestic transactions, with no im... Read more



Malaysia Postpones Mandatory E-Invoicing to 2027
 Other countries
Author: Ljubica Blagojević
Other countries
Author: Ljubica Blagojević
Malaysia has delayed mandatory MyInvois e-invoicing for businesses with RM1m–RM5m (€190k – €980k) turnover to 1 January 2027, with an extended penalty-free transition, citing readiness and cost concerns. This follows the increase of the exemption threshold to RM1 million, which removes smaller businesses from the scope and cancels the RM500k–RM1m rollout. Larger taxpayers remain on the existing ti... Read more


